| Commit | Line | Data |
|---|---|---|
| 898b5b63 MK |
1 | # **EDK II firmware for Intel(R) Quark SoC X1000 based platforms**\r |
| 2 | \r | |
| 3 | ## **Features**\r | |
| 4 | * UEFI firmware image with ability to enable/disable major features such as\r | |
| 5 | - Logging\r | |
| 6 | - Source level debug using [Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool](\r | |
| 7 | https://firmware.intel.com/develop/intel-uefi-tools-and-utilities/intel-uefi-development-kit-debugger-tool)\r | |
| 8 | - Boot Performance Measurements\r | |
| 9 | - UEFI Secure Boot with Physical Presence\r | |
| 10 | - TCG Measured Boot using TPM 1.2 hardware devices on I2C bus\r | |
| 11 | * Minimal firmware image for initial power-on and debug\r | |
| 12 | * UEFI Shell built into FLASH image\r | |
| 13 | * UEFI Linux operating system boot support from Micro SD FLASH\r | |
| 14 | * Hardware Support\r | |
| 15 | - [Intel(R) Quark SoC X1000 CPU](\r | |
| 16 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/embedded/products/quark/quark-x1000-datasheet.html)\r | |
| 17 | - [Intel(R) Galileo Development Board](\r | |
| 18 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/embedded/products/galileo/galileo-g1-datasheet.html)\r | |
| 19 | - [Intel(R) Galileo Gen 2 Development Board](\r | |
| 20 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/embedded/products/galileo/galileo-overview.html)\r | |
| 21 | - HPET Timer\r | |
| 22 | - Real Time Clock\r | |
| 23 | * Major I/O Subsystems\r | |
| 24 | - PCI including support for Mini PCI Express Cards\r | |
| 25 | - USB using EHCI and OHCI host controllers\r | |
| 26 | - Micro SD FLASH with FAT file system support\r | |
| 27 | - Serial UART up to 921600 baud for console, logging, and debug\r | |
| 28 | * ACPI Tables with ACPI S3 sleep state support\r | |
| 29 | * SMBIOS Tables\r | |
| 30 | \r | |
| 31 | ## **Windows Build Instructions**\r | |
| 32 | \r | |
| 33 | ### Pre-requisites\r | |
| 34 | \r | |
| 35 | * GIT client: Available from https://git-scm.com/downloads\r | |
| 36 | * Microsoft Visual Studio.\r | |
| 37 | - Visual Studio 2015 recommended and is used in the examples below.\r | |
| 38 | * Microsoft Windows Driver Development Kit 3790.1830\r | |
| 39 | - http://download.microsoft.com/download/9/0/f/90f019ac-8243-48d3-91cf-81fc4093ecfd/1830_usa_ddk.iso\r | |
| 40 | - Mount ISO image\r | |
| 41 | - Right click on ```x86\kitsetup.exe``` & choose **Run as administrator**\r | |
| 42 | - Install to C:\WINDDK\3790.1830\r | |
| 43 | - Uncheck all Component Groups\r | |
| 44 | - Expand Build Environment Component\r | |
| 45 | - Check Windows Driver Development Kit 16-bit Additional Build Tools\r | |
| 46 | - Install\r | |
| 47 | * ASL compiler: Available from http://www.acpica.org\r | |
| 48 | - Install into ```C:\ASL``` to match default tools_def.txt configuration.\r | |
| 42750cf1 | 49 | * Python 2.7: Available from http://www.python.org\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
50 | \r |
| 51 | Create a new directory for an EDK II WORKSPACE.\r | |
| 52 | \r | |
| 53 | The code block below shows the GIT clone operations required to pull the EDK II\r | |
| 42750cf1 | 54 | source tree and the edk2-non-osi repository that provides a binary file for the\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
55 | Quark Remote Management Unit (RMU).\r |
| 56 | \r | |
| 57 | Next it sets environment variables that must be set before running\r | |
| 58 | ```edksetup.bat```. Since content is being pulled from multiple repositories,\r | |
| 59 | the EDK II [Multiple Workspace](\r | |
| 60 | https://github.com/tianocore/tianocore.github.io/wiki/Multiple_Workspace)\r | |
| 61 | feature is used.\r | |
| 62 | \r | |
| 42750cf1 MK |
63 | Next, the EDK II BaseTools required to build firmware images are built.\r |
| 64 | \r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
65 | Next, the ```edksetup.bat``` file is run to complete the initialization of an\r |
| 66 | EDK II build environment. Two example build commands are shown. The first one\r | |
| 67 | in ```QuarkPlatformPlg/Quark.dsc``` builds a full UEFI firmware image that is\r | |
| 68 | able to boot the built-in UEFI Shell and Linux from a micro SD FLASH card. The\r | |
| 69 | second one in ```QuarkPlatformPkg/QuarkMin.dsc``` builds a minimal firmware\r | |
| 70 | image that is useful for initial power-on and debug of new features.\r | |
| 71 | \r | |
| 72 | ```cmd\r | |
| 73 | git clone https://github.com/tianocore/edk2.git\r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
74 | git clone https://github.com/tianocore/edk2-non-osi.git\r |
| 75 | \r | |
| 42750cf1 | 76 | set PYTHON_HOME=c:\Python27\r |
| 898b5b63 | 77 | set WORKSPACE=%CD%\r |
| 42750cf1 MK |
78 | set PACKAGES_PATH=%WORKSPACE%\edk2;%WORKSPACE%\edk2-non-osi\Silicon\Intel\r |
| 79 | set EDK_TOOLS_PATH=%WORKSPACE%\edk2\BaseTools\r | |
| 80 | cd %WORKSPACE%\edk2\r | |
| 898b5b63 | 81 | \r |
| 42750cf1 MK |
82 | BaseTools\toolsetup.bat Rebuild\r |
| 83 | \r | |
| 84 | edksetup.bat Rebuild\r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
85 | \r |
| 86 | build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc\r | |
| 87 | build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/QuarkMin.dsc\r | |
| 88 | ```\r | |
| 89 | \r | |
| 90 | ## **Linux Build Instructions**\r | |
| 91 | \r | |
| 92 | ### Pre-requisites\r | |
| 93 | \r | |
| 94 | * GIT client\r | |
| 95 | * GCC 4.9 compiler\r | |
| 96 | * ASL compiler: Available from http://www.acpica.org.\r | |
| 42750cf1 | 97 | * Python 2.7\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
98 | \r |
| 99 | Create a new directory for an EDK II WORKSPACE.\r | |
| 100 | \r | |
| 101 | The code block below shows the GIT clone operations required to pull the EDK II\r | |
| 42750cf1 MK |
102 | source tree and the edk2-non-osi repository that provides a binary file for the\r |
| 103 | Quark Remote Management Unit (RMU).\r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
104 | \r |
| 105 | Next it sets environment variables that must be set before running\r | |
| 106 | ```edksetup.bat```. Since content is being pulled from multiple repositories,\r | |
| 107 | the EDK II [Multiple Workspace](\r | |
| 108 | https://github.com/tianocore/tianocore.github.io/wiki/Multiple_Workspace)\r | |
| 109 | feature is used.\r | |
| 110 | \r | |
| 111 | Next, the EDK II BaseTools required to build firmware images are built.\r | |
| 112 | \r | |
| 42750cf1 | 113 | Next, the ```edksetup.sh``` file is run to complete the initialization of an\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
114 | EDK II build environment. Two example build commands are shown. The first one\r |
| 115 | in ```QuarkPlatformPlg/Quark.dsc``` builds a full UEFI firmware image that is\r | |
| 116 | able to boot the built-in UEFI Shell and Linux from a micro SD FLASH card. The\r | |
| 117 | second one in ```QuarkPlatformPkg/QuarkMin.dsc``` builds a minimal firmware\r | |
| 118 | image that is useful for initial power-on and debug of new features.\r | |
| 119 | \r | |
| 120 | ```sh\r | |
| 121 | git clone https://github.com/tianocore/edk2.git\r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
122 | git clone https://github.com/tianocore/edk2-non-osi.git\r |
| 123 | \r | |
| 124 | export WORKSPACE=$PWD\r | |
| 42750cf1 | 125 | export PACKAGES_PATH=$WORKSPACE/edk2:$WORKSPACE/edk2-non-osi/Silicon/Intel\r |
| 898b5b63 | 126 | export EDK_TOOLS_PATH=$WORKSPACE/edk2/BaseTools\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
127 | cd $WORKSPACE/edk2\r |
| 128 | \r | |
| 42750cf1 MK |
129 | make -C BaseTools\r |
| 130 | \r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
131 | . edksetup.sh BaseTools\r |
| 132 | \r | |
| 133 | build -a IA32 -t GCC49 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc\r | |
| 134 | build -a IA32 -t GCC49 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/QuarkMin.dsc\r | |
| 135 | ```\r | |
| 136 | \r | |
| 137 | ## **Build Features**\r | |
| 138 | \r | |
| 139 | The table below contains a summary of the build flags to enable or disable\r | |
| 140 | features on the build command line using ```-D``` flags.\r | |
| 141 | \r | |
| 142 | | **Define Name** | **Default Value** | **Supported Values** |\r | |
| 143 | | -------------------------- | ----------------- | -------------------- |\r | |
| 144 | | ```GALILEO``` | GEN2 | GEN1, GEN2 |\r | |
| 145 | | ```LOGGING``` | TRUE | TRUE, FALSE |\r | |
| 146 | | ```SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE``` | FALSE | TRUE, FALSE |\r | |
| 147 | | ```PERFORMANCE_ENABLE``` | FALSE | TRUE, FALSE |\r | |
| 148 | | ```SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE``` | FALSE | TRUE, FALSE |\r | |
| 149 | | ```MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE``` | FALSE | TRUE, FALSE |\r | |
| 150 | | ```TPM_12_HARDWARE``` | NONE | NONE, LPC, ATMEL_I2C, INFINEON_I2C |\r | |
| ff4e4b26 JY |
151 | | ```CAPSULE_ENABLE``` | FALSE | TRUE, FALSE |\r |
| 152 | | ```RECOVERY_ENABLE``` | FALSE | TRUE, FALSE |\r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
153 | \r |
| 154 | * ```GALILEO``` - Used to specify the type of Intel(R) Galileo board type. The\r | |
| 155 | default is ```GEN2``` for the [Intel(R) Galileo Gen 2 Development Board](\r | |
| 156 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/embedded/products/galileo/galileo-overview.html).\r | |
| 157 | The other supported value is ```GEN1``` for the [Intel(R) Galileo Development Board](\r | |
| 158 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/embedded/products/galileo/galileo-g1-datasheet.html).\r | |
| 159 | Add ```-D GALILEO=GEN1``` to the build command for [Intel(R) Galileo Development Board](\r | |
| 160 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/embedded/products/galileo/galileo-g1-datasheet.html).\r | |
| 161 | \r | |
| 162 | * ```LOGGING``` - Used to enable/disable logging messages from DEBUG() macros to\r | |
| 163 | a serial UART. The default is TRUE for enabled when the BUILDTARGET is DEBUG\r | |
| 164 | (```-b DEBUG```). The default is FALSE for disabled when the BUILDTARGET is\r | |
| 165 | not DEBUG (e.g. ```-b RELEASE```). Add ```-D LOGGING``` to the build command\r | |
| 166 | to force logging enabled. Add ```-D LOGGING=FALSE``` to force logging\r | |
| 167 | disabled.\r | |
| 168 | \r | |
| 169 | * ```SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE``` - Used to enable/disable source level debug using the\r | |
| 170 | [Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool](\r | |
| 171 | https://firmware.intel.com/develop/intel-uefi-tools-and-utilities/intel-uefi-development-kit-debugger-tool).\r | |
| 172 | The default is FALSE for disabled. Add ```-D SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE``` to the\r | |
| 173 | build command line to enable source level debug.\r | |
| 174 | \r | |
| 175 | * ```PERFORMANCE_ENABLE``` - Used to enable/disable boot performance measurement.\r | |
| 176 | The default is FALSE for disabled. Add ```-D PERFORMANCE_ENABLE``` to the\r | |
| 177 | build command line to enable boot performance measurement. When this feature\r | |
| 178 | is enabled, both ```LOGGING``` and ```SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE``` are automatically\r | |
| 179 | disabled so there is not boot time overhead from the serial UART for logging\r | |
| 180 | messages or the debug agent.\r | |
| 181 | \r | |
| 182 | * ```SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE``` - Used to enable/disable UEFI Secure Boot features.\r | |
| 183 | The default is FALSE for disabled. Add ```-D SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE``` to the\r | |
| 184 | build command line to enable UEFI Secure Boot features.\r | |
| 185 | \r | |
| 186 | * ```MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE``` - Used to enable/disable measurement of firmware\r | |
| 187 | code and data into a TPM 1.2 hardware device. The default is FALSE for\r | |
| 188 | disabled. Add ```-D MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE``` to the build command line to\r | |
| 189 | enable UEFI Secure Boot features.\r | |
| 190 | \r | |
| 191 | * ```TPM_12_HARDWARE``` - Used to specify the type of TPM 1.2 hardware device\r | |
| 192 | that is connected to the Galileo board. This define is valid if the measure\r | |
| 193 | boot feature is enabled using ```-D MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE```. The default is\r | |
| 194 | NONE for no TPM 1.2 hardware device connected. Add ```-D TPM_12_HARDWARE=LPC```\r | |
| 195 | for a TPM hardware device attached to an LPC bus (not supported on on Intel(R)\r | |
| 196 | Quark SoC X1000). Add ```-D TPM_12_HARDWARE=ATMEL_I2C``` for an\r | |
| 197 | [Atmel AT97SC3204T](http://www.atmel.com/devices/AT97SC3204T.aspx) or\r | |
| 198 | [Atmel AT97SC3205T](http://www.atmel.com/images/atmel-8883s-tpm-at97sc3205t-datasheet-summary.pdf)\r | |
| 199 | attached to the I2C bus of the Galileo Arduino header. Add\r | |
| 200 | ```-D TPM_12_HARDWARE=INFINION_I2C``` for an [Infineon SLB9645](\r | |
| 201 | http://www.infineon.com/dgdl/Infineon-TPM+SLB+9645-DS-v01_00-EN.pdf?fileId=5546d4625185e0e201518b83d0c63d7c)\r | |
| 202 | attached to the I2C bus of the Galileo Arduino header. The ATMEL_I2C setting\r | |
| 203 | has been tested with the [CryptoShield](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/13183)\r | |
| 204 | available from [SparkFun](https://www.sparkfun.com/).\r | |
| 205 | \r | |
| ff4e4b26 JY |
206 | * ```CAPSULE_ENABLE``` - Used to enable/disable capsule update features.\r |
| 207 | The default is FALSE for disabled. Add ```-D CAPSULE_ENABLE``` to the\r | |
| 208 | build command line to enable capsule update features.\r | |
| 209 | The build process generate capsule update image - QUARKFIRMWAREUPDATECAPSULEFMPPKCS7.Cap.\r | |
| 210 | The user need copy QUARKFIRMWAREUPDATECAPSULEFMPPKCS7.Cap and CapsuleApp.efi\r | |
| 211 | to a storage media attached to the Quark Board.\r | |
| 212 | Then the user can boot to shell and run ```CapsuleApp QUARKFIRMWAREUPDATECAPSULEFMPPKCS7.Cap```.\r | |
| 213 | In next reboot, the system firmware is updated.\r | |
| 214 | \r | |
| 215 | * ```RECOVERY_ENABLE``` - Used to enable/disable recovery features.\r | |
| 216 | The default is FALSE for disabled. Add ```-D RECOVERY_ENABLE``` to the\r | |
| 217 | build command line to enable recovery features.\r | |
| 218 | The build process generates the recovery capsule image - QUARKREC.Cap.\r | |
| 219 | Then the user need copy QUARKREC.Cap to a USB KEY, plug the USB KEY to the Quark Board.\r | |
| 220 | In next boot, if a user runs ForceRecovery.efi in shell, or if a user presses the RESET button during power on, warm reset or REBOOT,\r | |
| 221 | or if the FvMain is corrupted in flash, the system will boot into recovery mode.\r | |
| 898b5b63 MK |
222 | \r |
| 223 | ### **Example Build Commands**\r | |
| 224 | \r | |
| 225 | Default build with logging enabled:\r | |
| 226 | \r | |
| 227 | ```build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc```\r | |
| 228 | \r | |
| 229 | Release build with logging disabled:\r | |
| 230 | \r | |
| 231 | ```build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc -b RELEASE```\r | |
| 232 | \r | |
| 233 | Enable source level debugging:\r | |
| 234 | \r | |
| 235 | ```build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc -D SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE```\r | |
| 236 | \r | |
| 237 | Enable boot performance metrics:\r | |
| 238 | \r | |
| 239 | ```build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc -D PERFORMANCE_ENABLE```\r | |
| 240 | \r | |
| 241 | Enable UEFI Secure Boot features:\r | |
| 242 | \r | |
| 243 | ```build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc -D UEFI_SECURE_BOOT```\r | |
| 244 | \r | |
| 245 | Enable UEFI Secure Boot and Measured Boot using Atmel I2C TPM hardware device:\r | |
| 246 | \r | |
| 8716ac53 | 247 | ```build -a IA32 -t VS2015x86 -p QuarkPlatformPkg/Quark.dsc -D UEFI_SECURE_BOOT -D MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE -D TPM_12_HARDWARE=ATMEL_I2C```\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
248 | \r |
| 249 | ## **FLASH Update using DediProg SF100**\r | |
| 250 | \r | |
| 251 | Once the sources have been downloaded, an EDK II build environment established,\r | |
| 252 | and an EDK II firmware image has been built, the EDK II firmware image needs to\r | |
| 253 | installed into the FLASH device on the target Galileo development board. One\r | |
| 254 | way to do this is with the [Dediprog SF100 IC Programmer](\r | |
| 255 | http://www.dediprog.com/pd/spi-flash-solution/SF100).\r | |
| 256 | \r | |
| 257 | * Install the DediProg SF100 software.\r | |
| 258 | \r | |
| 259 | * Connect the DediProg SF100 to the Galileo development board.\r | |
| 260 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 261 |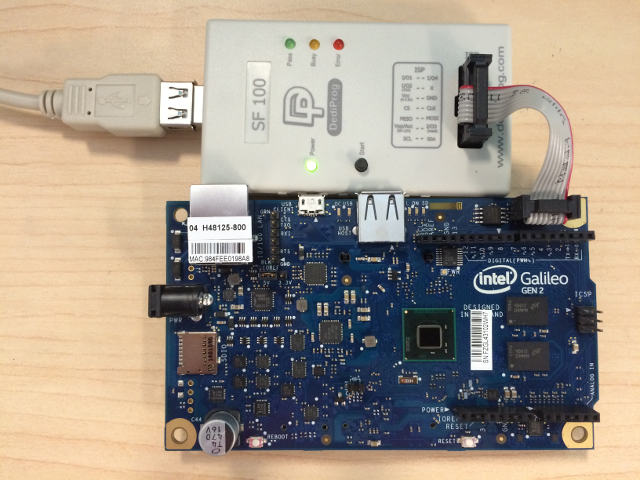 \r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
262 | \r |
| 263 | * Make sure ```dpcmd.exe``` is in ```PATH```\r | |
| 264 | \r | |
| 265 | ```PATH=%PATH%;"c:\Program Files (x86)\DediProg\SF100"```\r | |
| 266 | \r | |
| 267 | * **NOTE**: It is recommended that the FLASH image that was shipped with the\r | |
| 268 | Galileo development board be read and saved before updating FLASH image. The\r | |
| 269 | command shown below read the FLASH image and saves it to the file\r | |
| 270 | called ```GalileoOriginalFirmware.bin```.\r | |
| 271 | \r | |
| 272 | ```dpcmd.exe -r GalileoOriginalFirmware.bin```\r | |
| 273 | \r | |
| 274 | * Update FLASH image using either the DediProg SF100 GUI or ```dpcmd.exe```.\r | |
| 275 | - Example update of Galileo firmware image when BUILDTARGET is DEBUG (default)\r | |
| 276 | \r | |
| 277 | ```dpcmd.exe -u%WORKSPACE%\Build\Quark\DEBUG_VS2015x86\FV\QUARK.fd ```\r | |
| 278 | \r | |
| 279 | - Example update of Galileo firmware image when BUILDTARGET is RELEASE\r | |
| 280 | (```-b RELEASE```)\r | |
| 281 | \r | |
| 282 | ```dpcmd.exe -u%WORKSPACE%\Build\Quark\RELEASE_VS2015x86\FV\QUARK.fd ```\r | |
| 283 | \r | |
| 284 | ## **Setting up a Serial Console and Booting to UEFI Shell**\r | |
| 285 | \r | |
| 286 | After the FLASH is updated on Galileo, a serial cable is connected between the\r | |
| 287 | host system and the Galileo target. A serial terminal emulator (such as\r | |
| 288 | [Tera Term](https://en.osdn.jp/projects/ttssh2/releases/)) can be used to see\r | |
| 289 | the logging messages from DEBUG() macros and the serial console for the UEFI\r | |
| 290 | Boot Manager, UEFI Shell, and operating system.\r | |
| 291 | \r | |
| 292 | The default serial communication parameters for the Intel(R) Galileo Gen 2\r | |
| 293 | Development Board is 921600,n,8,1 with no hardware flow control.\r | |
| 294 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 295 | 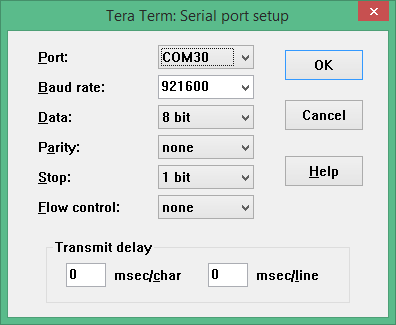\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
296 | \r |
| 297 | The default serial communication parameters for the Intel(R) Galileo Development\r | |
| 298 | Board is 461800,n,8,1 with no hardware flow control.\r | |
| 299 | \r | |
| 300 | The following changes to the [Tera Term](https://en.osdn.jp/projects/ttssh2/releases/)\r | |
| 301 | configuration files are recommended for UEFI serial console compatibility.\r | |
| 302 | Some of the later use cases involve using the TCPIP mode, so some of these\r | |
| 303 | recommendation apply to the TCPIP use cases.\r | |
| 304 | \r | |
| 305 | * TERATERM.INI - Set terminal size to 80 x 25 and terminal settings to UTF8.\r | |
| 306 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 307 | 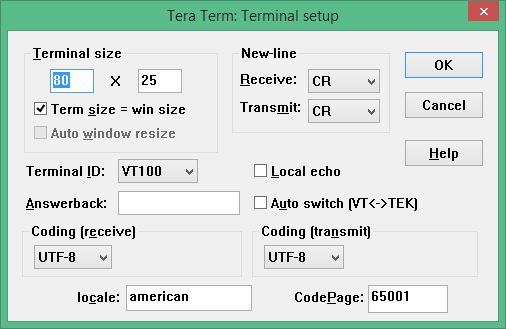\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
308 | \r |
| 309 | * TERATERM.INI - Set font type to Terminal to support box drawing glyphs.\r | |
| 310 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 311 | 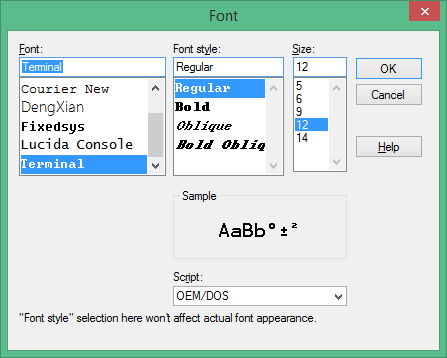\r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
312 | \r |
| 313 | * TERATERM.INI - Disable line mode to make TCPIP mode work like COM port mode.\r | |
| 314 | \r | |
| 315 | ```ini\r | |
| 316 | ; Line at a time mode\r | |
| 317 | EnableLineMode=off\r | |
| 318 | ```\r | |
| 319 | \r | |
| 320 | * KEYBOARD.CNF - Disable VT function keys for F5..F10\r | |
| 321 | \r | |
| 322 | ```ini\r | |
| 323 | [VT function keys]\r | |
| 324 | ;F6 key\r | |
| 325 | ;F6=64\r | |
| 326 | ;F7 key\r | |
| 327 | ;F7=65\r | |
| 328 | ;F8 key\r | |
| 329 | ;F8=66\r | |
| 330 | ;F9 key\r | |
| 331 | ;F9=67\r | |
| 332 | ;F10 key\r | |
| 333 | ;F10=68\r | |
| 334 | ```\r | |
| 335 | \r | |
| 336 | * KEYBOARD.CNF - Disable X function keys for F1..F4\r | |
| 337 | \r | |
| 338 | ```ini\r | |
| 339 | [X function keys]\r | |
| 340 | ; F1 key\r | |
| 341 | XF1=off\r | |
| 342 | ; F2 key\r | |
| 343 | ;XF2=60\r | |
| 344 | XF2=off\r | |
| 345 | ; F3 key\r | |
| 346 | ;XF3=61\r | |
| 347 | XF3=off\r | |
| 348 | ; F4 key\r | |
| 349 | ;XF4=62\r | |
| 350 | XF4=off\r | |
| 351 | ; F5 key\r | |
| 352 | ;XF5=63\r | |
| 353 | ```\r | |
| 354 | \r | |
| 355 | * KEYBOARD.CNF - Add UEFI serial console sequences for F1..F10\r | |
| 356 | \r | |
| 357 | ```ini\r | |
| 358 | [User keys]\r | |
| 359 | User1=59,0,$1B[M\r | |
| 360 | User2=60,0,$1B[N\r | |
| 361 | User3=61,0,$1B[O\r | |
| 362 | User4=62,0,$1B[P\r | |
| 363 | User5=63,0,$1B[Q\r | |
| 364 | User6=64,0,$1B[R\r | |
| 365 | User7=65,0,$1B[S\r | |
| 366 | User8=66,0,$1B[T\r | |
| 367 | User9=67,0,$1B[U\r | |
| 368 | User10=68,0,$1B[V\r | |
| 369 | ```\r | |
| 370 | \r | |
| 371 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board, and the logging messages\r | |
| 372 | should be seen, followed by 5 second countdown, followed by an automatic boot to\r | |
| 373 | the built-in UEFI Shell.\r | |
| 374 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 375 | \r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
376 | \r |
| 377 | ## **Source Level Debug Using Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool**\r | |
| 378 | \r | |
| 379 | ### Pre-requisites\r | |
| 380 | \r | |
| 381 | * Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool User Manual for Ver 1.5 or higher:\r | |
| 382 | Available from https://firmware.intel.com/develop/intel-uefi-tools-and-utilities/intel-uefi-development-kit-debugger-tool\r | |
| 383 | * Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool Ver 1.5 or higher: Available from\r | |
| 384 | https://firmware.intel.com/develop/intel-uefi-tools-and-utilities/intel-uefi-development-kit-debugger-tool\r | |
| 385 | * [Tera Term](https://en.osdn.jp/projects/ttssh2/releases/) or other serial\r | |
| 386 | terminal emulator with TCPIP support\r | |
| 387 | \r | |
| 388 | Follow instructions in Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool User manual\r | |
| 389 | to setup host system.\r | |
| 390 | \r | |
| 391 | Build a firmware image with SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE enabled\r | |
| 392 | (```-D SOURCE_DEBUG_ENABLE```). This will select the appropriate libraries,\r | |
| 393 | debug agent, and PCDs for Galileo. Galileo does not support a USB 2.0 debug\r | |
| 394 | port, so only the UART based communications library is used.\r | |
| 395 | \r | |
| 396 | Use Dediprog SF100 to update the Galileo development board FLASH image.\r | |
| 397 | \r | |
| 398 | Update the ```[Debug Port]``` section of the SoftDebugger.ini file with the host\r | |
| 399 | side UART configuration settings. The following example uses COM5, which must\r | |
| 400 | be updated with the COM port the Galileo target is attached. The following\r | |
| 401 | example also shows a baud rate of 921600 which is correct for a Galileo Gen 2.\r | |
| 402 | If a Galileo Gen 1 is being used, set the baud rate to 460800. By default, the\r | |
| 403 | Galileo console is redirected to TCPIP port 20715.\r | |
| 404 | \r | |
| 405 | ```ini\r | |
| 406 | [Debug Port]\r | |
| 407 | Channel = Serial\r | |
| 408 | Port = COM5\r | |
| 409 | FlowControl = 0\r | |
| 410 | BaudRate = 921600\r | |
| 411 | Server =\r | |
| 412 | ```\r | |
| 413 | \r | |
| 414 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board and run a command script with\r | |
| 415 | the contents below to start a Tera Term session on TCPIP port 20715 and start\r | |
| 416 | the Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool using UART connection between\r | |
| 417 | the host and target and WinDbg. The REBOOT button on the Galileo development\r | |
| 418 | board may need to be pressed for the debugger to perform the initial connect.\r | |
| 419 | \r | |
| 420 | ```cmd\r | |
| 421 | start "Console" /B "c:\Program Files (x86)\teraterm\ttermpro.exe" localhost:20715 /nossh\r | |
| 422 | start "Debugger" /B "C:\Program Files (x86)\Intel\Intel(R) UEFI Development Kit Debugger Tool\eXdi.exe" /LaunchWinDbg\r | |
| 423 | ```\r | |
| 424 | \r | |
| 425 | The figure below should be seen when a connection is made. The SoftDebugger\r | |
| 426 | Debug Console window shows the status of the connection between the host and the\r | |
| 427 | target. The Tera Term window shows the console output from the SEC phase until\r | |
| 428 | the debug agent is initialized. The WinDbg window shows that the debugger is\r | |
| 429 | connected and the WinDbg application can be used for run control, breakpoint\r | |
| 430 | management, and viewing call stacks, local variables, global variables, etc.\r | |
| 431 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 432 | \r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
433 | \r |
| 434 | ## **Debug Using Intel(R) System Debugger using OpenOCD**\r | |
| 435 | \r | |
| 436 | Setup hardware and software components following the instructions in the article at:\r | |
| 437 | https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/using-intel-system-debugger-with-openocd\r | |
| 438 | \r | |
| 439 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board.\r | |
| 440 | \r | |
| 441 | The following batch file starts Tera Term serial console on COM5 at 921600 baud,\r | |
| 442 | starts OpenOCD using a Flyswatter2, and starts Intel(R) System Studio Debugger.\r | |
| 443 | Select the **Connect** button to complete the host to target connection.\r | |
| 444 | \r | |
| 445 | ```cmd\r | |
| 446 | set OPENOCD="C:\Program Files (x86)\IntelSWTools\system_studio_for_windows_2016.0.023\debugger\openocd"\r | |
| 447 | start "Console" /B "c:\Program Files (x86)\teraterm\ttermpro.exe" /C=5 /BAUD=921600\r | |
| 448 | start "OpenOcd" /B %OPENOCD%\bin\openocd.exe -f ..\scripts\interface\ftdi\flyswatter2.cfg -f ..\scripts\board\quark_x10xx_board.cfg\r | |
| 449 | call "C:\Program Files (x86)\IntelSWTools\System Debugger 2016\system_debugger\start_xdb_gdb_remote.bat"\r | |
| 450 | ```\r | |
| 451 | \r | |
| 452 | When **Reset Target** is selected, the Galileo development board does not always\r | |
| 453 | halt at the first instruction at the reset vector. If debug is required from\r | |
| 454 | the first instruction of the reset vector, then update the file\r | |
| 455 | ```UefiCpuPkg/SecCore/Ia32/ResetVector.asm``` and change the two NOP\r | |
| 456 | instructions at the label ```ResetHandler:``` to ```JMP $```. This puts the CPU\r | |
| 457 | into a wait loop until the debugger is connected and the debugger is used to set\r | |
| 458 | instruction pointer to the next instruction.\r | |
| 459 | \r | |
| 460 | ```\r | |
| 461 | ;\r | |
| 462 | ; For IA32, the reset vector must be at 0xFFFFFFF0, i.e., 4G-16 byte\r | |
| 463 | ; Execution starts here upon power-on/platform-reset.\r | |
| 464 | ;\r | |
| 465 | ResetHandler:\r | |
| 466 | ; nop\r | |
| 467 | ; nop\r | |
| 468 | jmp $\r | |
| 469 | ApStartup:\r | |
| 470 | ;\r | |
| 471 | ; Jmp Rel16 instruction\r | |
| 472 | ; Use machine code directly in case of the assembler optimization\r | |
| 473 | ; SEC entry point relative address will be fixed up by some build tool.\r | |
| 474 | ;\r | |
| 475 | ; Typically, SEC entry point is the function _ModuleEntryPoint() defined in\r | |
| 476 | ; SecEntry.asm\r | |
| 477 | ;\r | |
| 478 | DB 0e9h\r | |
| 479 | DW -3\r | |
| 480 | ```\r | |
| 481 | \r | |
| 482 | ## **Install, Configure, and Boot Linux**\r | |
| 483 | \r | |
| 484 | * Download SD Card Linux Image: Available at\r | |
| 485 | http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/boards-and-kits/intel-galileo-boards/000005614.html\r | |
| 486 | * Extract the SD Card Linux Image to a FAT formatted Micro SD FLASH device\r | |
| 487 | * Install Micro SD FLASH device into Galileo development board\r | |
| 488 | \r | |
| 489 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board and boot to the UEFI Shell.\r | |
| 490 | \r | |
| 491 | From the UEFI Shell execute the following commands to copy the GRUB EFI boot\r | |
| 492 | loader to ```\efi\boot\bootia32.efi```. This allows the UEFI Boot Manager, on\r | |
| 493 | all future boots, to auto detect that the Micro SD FLASH device is bootable.\r | |
| 494 | \r | |
| 495 | ```\r | |
| 496 | Shell> connect -r\r | |
| 497 | Shell> map -r\r | |
| 498 | Shell> fs0:\r | |
| 499 | FS0:> mkdir efi\r | |
| 500 | FS0:> mkdir efi\boot\r | |
| 501 | FS0:> cp grub.efi efi\boot\bootia32.efi\r | |
| 502 | ```\r | |
| 503 | \r | |
| 504 | The GRUB boot loader is set to a UART baud rate of 115200. A couple changes are\r | |
| 505 | required to change the baud rate to 460800 for Galileo Gen 1 or 921600 for\r | |
| 506 | Galileo Gen 2. From the UEFI Shell, execute the following commands to make a\r | |
| 507 | backup copy and edit the GRUB configuration file.\r | |
| 508 | \r | |
| 509 | ```\r | |
| 510 | FS0:> cp boot\grub\grub.conf boot\grub\grub.conf.org\r | |
| 511 | FS0:> edit boot\grub\grub.conf\r | |
| 512 | ```\r | |
| 513 | \r | |
| 514 | * Delete the lines associated with the boot option with the following title.\r | |
| 515 | \r | |
| 516 | ```\r | |
| 517 | title Clanton SVP kernel-SPI initrd-SPI IMR-On IO-APIC/HPET NoEMU\r | |
| 518 | ```\r | |
| 519 | \r | |
| 520 | * Replace the two instances of 115200 in the following line to 460800 for\r | |
| 521 | Galileo Gen 1 or 921600 for Galileo Gen 2.\r | |
| 522 | \r | |
| 523 | ```\r | |
| 524 | kernel /bzImage root=/dev/ram0 console=ttyS1,115200n8 earlycon=uart8250,mmio32,$EARLY_CON_ADDR_REPLACE,115200n8 reboot=efi,warm apic=debug rw LABEL=boot debugshell=5 rootimage=image-full-galileo-clanton.ext3\r | |
| 525 | ```\r | |
| 526 | * Press F3 to save the file\r | |
| 527 | * Run the ```exit``` command to exit from the UEFI Shell and return to the\r | |
| 528 | UEFI Boot Manager\r | |
| 529 | * Select **Boot Manager**\r | |
| 530 | * Select **UEFI Misc Device** for the Micro SD FLASH device.\r | |
| 531 | * GRUB should run and Linux should boot with serial log messages.\r | |
| 532 | * When the serial log messages stop, change the Tera Term baud rate to 115200\r | |
| 533 | * Login as ```root```. No password is required.\r | |
| 534 | * Use ```vi``` to edit ```/etc/inittab```\r | |
| 535 | * Change the baud rate of ttyS1 from 115200 to 460800 for Galileo Gen 1 or\r | |
| 536 | 921600 for Galileo Gen 2. The line that need to be updated is shown below\r | |
| 537 | \r | |
| 538 | ```\r | |
| 539 | S:2345:respawn:/sbin/getty 115200 ttyS1\r | |
| 540 | ```\r | |
| 541 | \r | |
| 542 | * Save the updated ```/etc/inittab```\r | |
| 543 | * Run ```reboot -f``` to shutdown Linux and reboot the platform.\r | |
| 544 | * Set the Tera Term baud rate back to 460800 for Galileo Gen 1 or 921600 for\r | |
| 545 | Galileo Gen 2.\r | |
| 546 | \r | |
| 547 | After these changes both the EDK II firmware and the Linux operating system use\r | |
| 548 | the same baud rate.\r | |
| 549 | \r | |
| 550 | ### **Testing ACPI S3 Sleep**\r | |
| 551 | \r | |
| 552 | The ACPI S3 Sleep and Resume feature can be tested on a Galileo development\r | |
| 553 | board using the Real Time Clock (RTC) for a wake event. The shell script shown\r | |
| 554 | below arms the RTC wake alarm 10 seconds in the future and puts the system to\r | |
| 555 | sleep. A shorter time in seconds can be passed in as the first argument to the\r | |
| 556 | script, but do not use times shorter than 2 or 3 seconds.\r | |
| 557 | \r | |
| 558 | **NOTE**: The stmmac module is unloaded because the module is not compatible\r | |
| 559 | with S3 resume.\r | |
| 560 | \r | |
| 561 | ```sh\r | |
| 562 | #\r | |
| 563 | # Unload NIC driver that causes S3 to fail\r | |
| 564 | #\r | |
| 565 | rmmod stmmac\r | |
| 566 | \r | |
| 567 | #\r | |
| 568 | # Disable RTC wake alarm\r | |
| 569 | #\r | |
| 570 | echo 0 > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm\r | |
| 571 | \r | |
| 572 | #\r | |
| 573 | # Compute wake time that is $1 seconds in the future\r | |
| 574 | #\r | |
| 575 | let WakeTime=`date '+%s'`\r | |
| 576 | echo $WakeTime\r | |
| 577 | if ["$1" = ""]; then\r | |
| 578 | let WakeTime=$WakeTime+10\r | |
| 579 | else\r | |
| 580 | let WakeTime=$WakeTime+$1\r | |
| 581 | fi\r | |
| 582 | echo $WakeTime\r | |
| 583 | \r | |
| 584 | #\r | |
| 585 | # Enable RTC wake alarm $1 seconds in the future\r | |
| 586 | #\r | |
| 587 | echo $WakeTime > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm\r | |
| 588 | \r | |
| 589 | #\r | |
| 590 | # Put systems into ACPI S3 sleep state\r | |
| 591 | #\r | |
| 592 | echo mem > /sys/power/state\r | |
| 593 | ```\r | |
| 594 | \r | |
| 595 | ## **UEFI Secure Boot Feature and Physical Presence**\r | |
| 596 | \r | |
| 597 | Build a firmware image with SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE enabled\r | |
| 598 | (```-D SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE```). This builds in support for UEFI authenticated\r | |
| 599 | variables, UEFI image verification, and UEFI Secure Boot configuration screens\r | |
| 600 | in the Device Manager. In order to change the UEFI Secure Boot configuration,\r | |
| 601 | the user must assert physical presence. The Galileo development board only has\r | |
| 602 | two push buttons (REBOOT and RESET). The REBOOT button unconditionally reboots\r | |
| 603 | the platform. The RESET button asserts the reset signal on the Arduino header\r | |
| 604 | and is also connected to a GPIO pin, so the state of the RESET button can be\r | |
| 605 | read. The user asserts physical presence by holding the RESET button while the\r | |
| 606 | Galileo development board boots, or by holding the RESET button while selecting\r | |
| 607 | the **Secure Boot Configuration** option in the Device Manager.\r | |
| 608 | \r | |
| 609 | Use Dediprog SF100 to update the Galileo development board FLASH image.\r | |
| 610 | \r | |
| 611 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board and boot to the UEFI Boot\r | |
| 612 | Manager by pressing F2 or running the ```exit``` command from the UEFI Shell.\r | |
| 613 | Select **Device Manager** and then**Secure Boot Configuration**. Change\r | |
| 614 | **Customize Secure Boot** to **Customized** and then select **Custom Secure Boot\r | |
| 615 | Options**. If **Custom Secure Boot Options** can not be selected, then physical\r | |
| 616 | presence was not asserted using one of two methods listed above. Assert\r | |
| 617 | physical presence and try again.\r | |
| 618 | \r | |
| 619 | The **Custom Secure Boot Options** screen allows the Galileo development board\r | |
| 620 | to be enrolled into UEFI Secure Boot. See [How to Sign UEFI Drivers & Application V1.31](\r | |
| 621 | http://sourceforge.net/projects/edk2/files/General%20Documentation/SigningUefiImages%20-v1dot31.pdf/download)\r | |
| 622 | in the [SecurityPkg Wiki](https://github.com/tianocore/tianocore.github.io/wiki/SecurityPkg)\r | |
| 623 | for details on how to complete the UEFI Secure Boot enrollment.\r | |
| 624 | \r | |
| 625 | ## **Enable Measured Boot Feature using Atmel I2C TPM on CryptoShield**\r | |
| 626 | \r | |
| 627 | Build a firmware image with MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE enabled\r | |
| 628 | (```-D MEASURED_BOOT_ENABLE```) and TPM_12_HARDWARE set to ATMEL_I2C\r | |
| 629 | (```-D TMP_12_HARDWARE=ATMEL_I2C```). This builds in the TCG PEIM and DXE\r | |
| 630 | modules and uses the library for the Atmel I2C TPM hardware device.\r | |
| 631 | \r | |
| 632 | Use Dediprog SF100 to update the Galileo development board FLASH image.\r | |
| 633 | \r | |
| 634 | Attach the CryptoShield to the Arduino header of the Galileo development board\r | |
| 635 | as shown below.\r | |
| 636 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 637 | \r |
| 898b5b63 MK |
638 | \r |
| 639 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board and boot to the UEFI Shell.\r | |
| 640 | In the boot logging messages, messages similar to the following should be seen\r | |
| 641 | as the Atmel I2C TPM hardware device is detected and used to measure the\r | |
| 642 | contents of firmware volumes and firmware tables.\r | |
| 643 | \r | |
| 644 | ```\r | |
| 645 | Loading PEIM at 0x0000FC75188 EntryPoint=0x0000FC75260 TrEEConfigPei.efi\r | |
| 646 | PROGRESS CODE: V03020002 I0\r | |
| 647 | TrEEConfiguration.TpmDevice from Setup: 1\r | |
| 648 | DetectTpmDevice:\r | |
| 649 | TpmDevice final: 1\r | |
| 650 | TpmDevice PCD: 8B01E5B6-4F19-46E8-AB93-1C53671B90CC\r | |
| 651 | . . .\r | |
| 652 | Loading PEIM at 0x0000FC70190 EntryPoint=0x0000FC70260 TcgPei.efi\r | |
| 653 | PROGRESS CODE: V03020002 I0\r | |
| 654 | Install PPI: E9DB0D58-D48D-47F6-9C6E-6F40E86C7B41\r | |
| 655 | Install PPI: A030D115-54DD-447B-9064-F206883D7CCC\r | |
| 656 | PROGRESS CODE: V03020003 I0\r | |
| 657 | The FV which is measured by TcgPei starts at: 0xFFF10000\r | |
| 658 | The FV which is measured by TcgPei has the size: 0xF0000\r | |
| 659 | The FV which is measured by TcgPei starts at: 0xFFD00000\r | |
| 660 | The FV which is measured by TcgPei has the size: 0x1E0000\r | |
| 661 | . . .\r | |
| 662 | Loading driver at 0x0000F620000 EntryPoint=0x0000F620260 TcgDxe.efi\r | |
| 663 | . . .\r | |
| 664 | TPM TcgDxe Measure Data when ReadyToBoot\r | |
| 665 | ```\r | |
| 666 | See the [SecurityPkg Wiki](https://github.com/tianocore/tianocore.github.io/wiki/SecurityPkg)\r | |
| 667 | for additional details on EDK II TPM support\r | |
| 668 | \r | |
| 669 | ## **Measuring Boot Performance**\r | |
| 670 | \r | |
| 671 | Build a firmware image with PERFORMANCE_ENABLE enabled\r | |
| 672 | (```-D PERFORMANCE_ENABLE```). This builds in the UEFI Shell and the DP.EFI\r | |
| 673 | (Dump Performance) into a firmware volume and also includes a simple file system\r | |
| 674 | driver for firmware volumes so the DP.EFI command can be run out of the FLASH.\r | |
| 675 | \r | |
| 676 | Use Dediprog SF100 to update the Galileo development board FLASH image.\r | |
| 677 | \r | |
| 678 | Connect power adapter to Galileo development board and let it boot to the UEFI\r | |
| 679 | Shell. Then use the REBOOT button or the ```reset``` UEFI Shell command to\r | |
| 680 | reboot the Galileo development board. The first boot after a FLASH update does\r | |
| 681 | extra work that is only performed one time. In order to get correct performance\r | |
| 682 | measurements, use the 2nd or later boots. After the 2nd boot, run the\r | |
| 683 | ```dp -s``` command. The output should look similar to the figure below.\r | |
| 684 | \r | |
| 33e0f9a7 | 685 | \r |